Diagnosing ADHD
To be diagnosed with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), individuals must meet the following criteria, adapted from DSM-5.1,3

Evaluating children vs adults
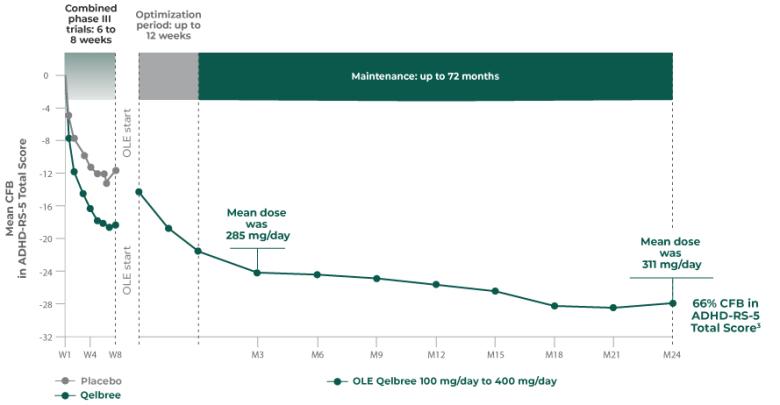
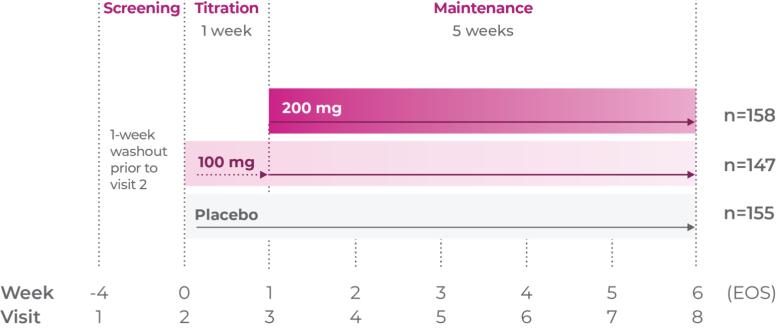
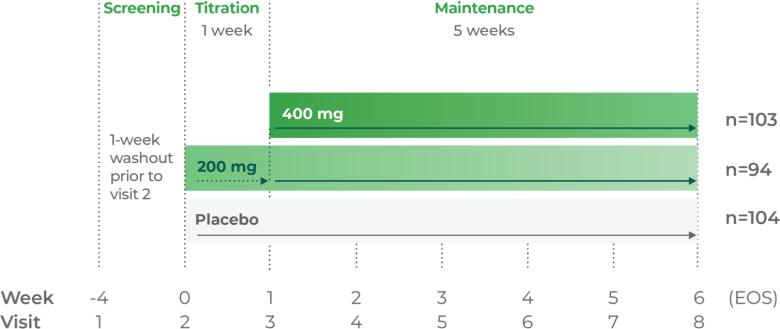
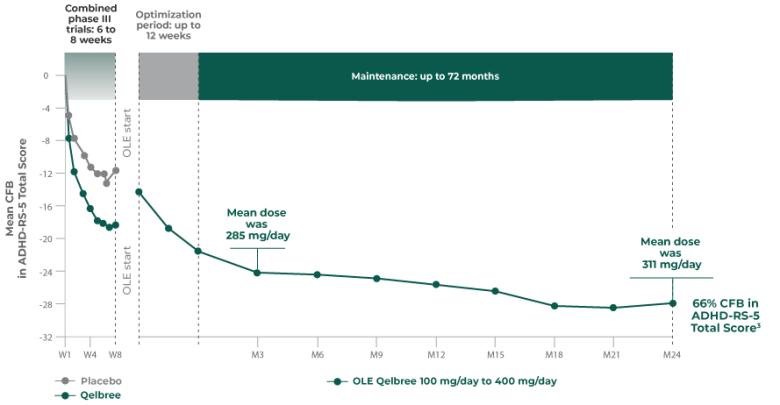
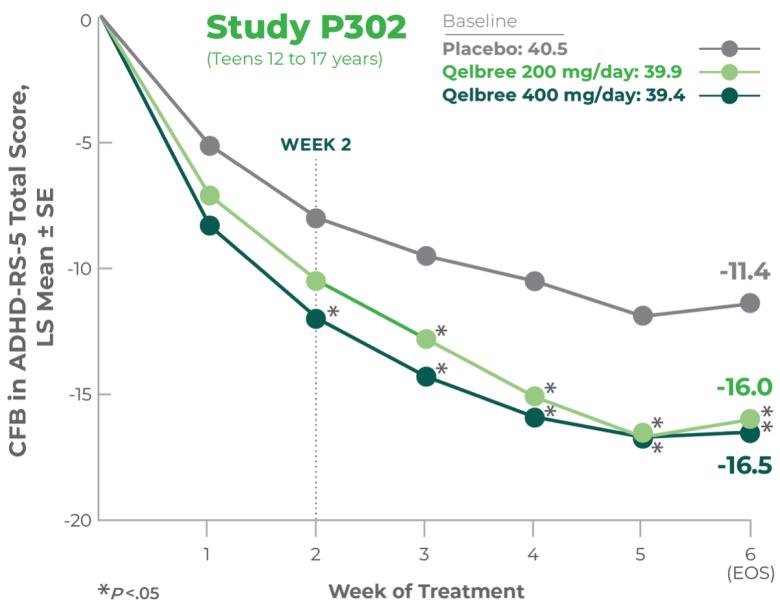
The ADHD rating scale 5 (ADHD-RS-5) is a rating scale specifically for children and adolescents with ADHD that has been updated to correspond with the DSM-5. The ADHD-RS-5 has several versions which correspond to different age groups (5-10 years old and 11-17 years old) as well as different settings (home and school).
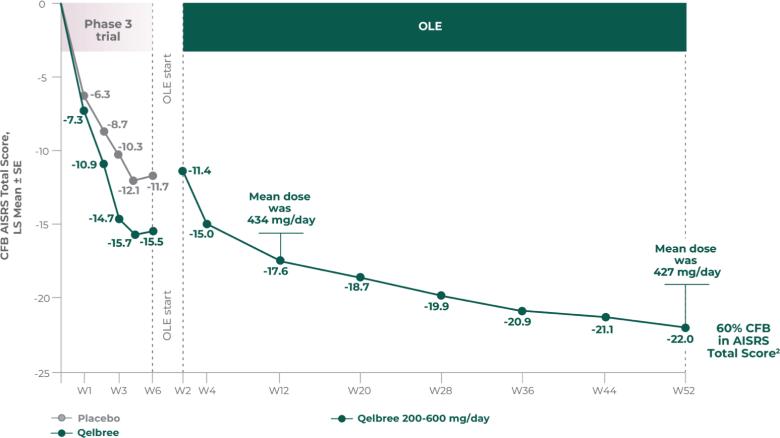
The Adult ADHD Investigator Symptom Rating Scale (AISRS) measures aspects of ADHD in adults that are consistent with the 18 DSM-5 symptoms.3
Both scales measure how ADHD symptoms can affect behavior such as hyperactivity/impulsivity, restlessness, and inattention.1-3
The diagnosis of ADHD in pediatrics
In order to be diagnosed with ADHD, 6 or more symptoms of inattention and/or hyperactivity/impulsivity must have persisted for at least 6 months to a degree that is inconsistent with developmental level and that negatively impacts directly on social and academic/occupational activities.1

The diagnosis of ADHD in older adolescents and adults
In order for people age 17 and older to be diagnosed with ADHD, 5 or more symptoms of inattention and/or hyperactivity/impulsivity must be present and negatively impacting directly on social and academic/occupational activities. Symptoms must have started before age 12.1
What to look for
Symptoms of inattention1,3
- Makes careless mistakes/lacks attention to detail
- Lacks sustained attention in tasks or fun activities
- Poor listener, even in the absence of obvious distraction
- Fails to follow through on tasks and instructions
- Difficulty with organization, time management, and deadlines
- Avoids tasks requiring sustained mental effort
- Loses things necessary for tasks or activities
- Easily distracted (including unrelated thoughts)
- Forgetful in daily activities
- Procrastinates and puts off tasks until the last moment possible
Symptoms of hyperactivity/impulsivity1
- Fidgets, taps hands, or squirms in seat
- Leaves seat in situations when remaining seated is expected
- Excessive running/climbing or feelings of restlessness
- Often “on the go”; acting as if “driven by a motor”
- Difficulty with quiet, leisure activities
- Excessive talking
- Blurts out answers before questions are even completed
- Difficulty waiting turn
- Interrupts or intrudes on others

Several ADHD symptoms must be present in 1 or more settings1
In order to diagnose ADHD, symptoms must be persistent; confirmation of substantially impacting symptoms across settings typically cannot be accurately assessed without consulting observers who have seen the individual in the setting.
Symptoms may vary depending on setting/context. Below, you will find some examples of how ADHD may affect individuals at home, at school, at work, and in relationships and social settings.
At home1
- Is forgetful doing chores
- Has difficulty keeping materials and belongings in order
- Reluctant to engage in tasks that require sustained mental effort, such as homework
- Several inattentive or hyperactive impulsive symptoms are present in one or more settings (e.g., at home, school, or work; with friends or relatives; in other activities)
At school or work1
- Does not follow through on instructions and fails to complete tasks
- Overlooks or misses details
- Is often restless and leaves seat inappropriately
- There is clear evidence that the symptoms interfere with, or reduce the quality of, social, academic, or occupational functioning
In relationships and social settings1
- Does not seem to listen when spoken to directly
- Cannot wait for turn in conversation
- May intrude into, or take over, what others are doing
- Has a difficult time making or maintaining friendships or romantic relationships

These are not the complete diagnostic criteria. Please see DSM-5 for full diagnostic criteria. It is important to note that diagnosis should be based on a complete clinical history of the patient.