Proven efficacy
Significant reduction in AISRS total score from CFB to EOS (6 weeks)1
Adults 18 years and older
Inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity symptom score reductions observed as early as week 2.2
Qelbree was studied in 4 clinical trials. In the flexible-dose study of adults 18 to 65 years of age, ADHD symptom score reductions were statistically significant in patients taking Qelbree, beginning at week 2.2

Qelbree is the first novel, non-stimulant treatment approved for adult ADHD in over 20 years1,3,4
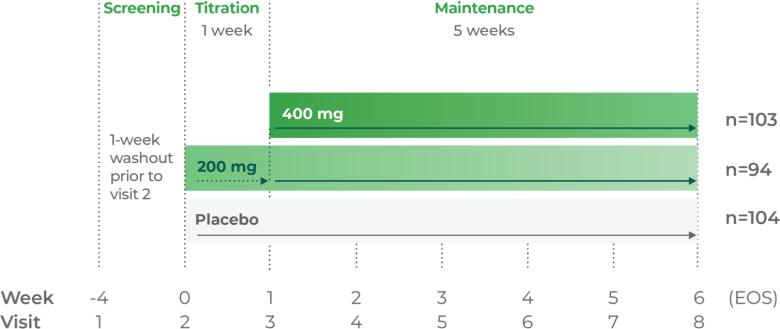
Phase III trial methodology1
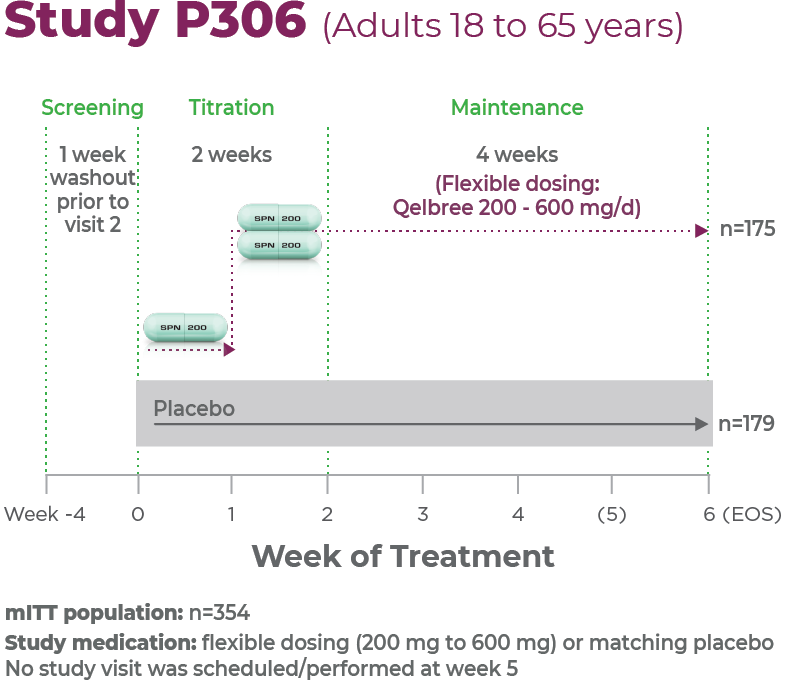
The clinical trial was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, parallel-group, flexible-dose study.
Primary endpoint1
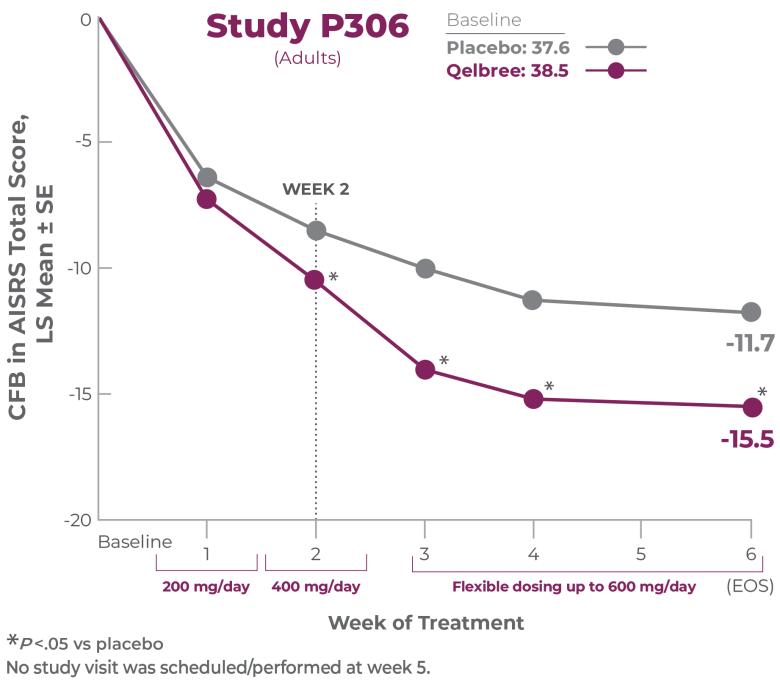
CFB to EOS in AISRS total score, Qelbree treatment group.
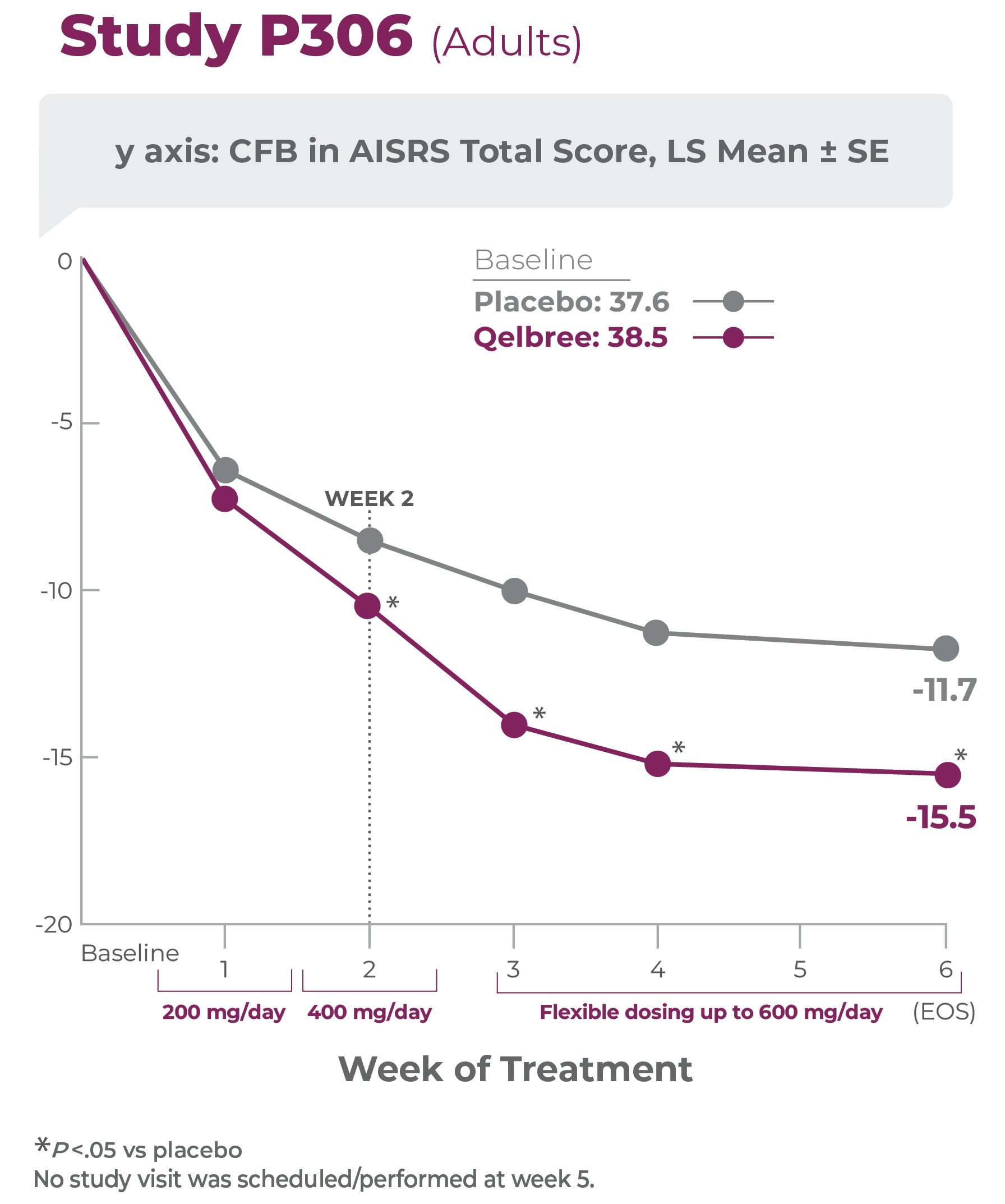
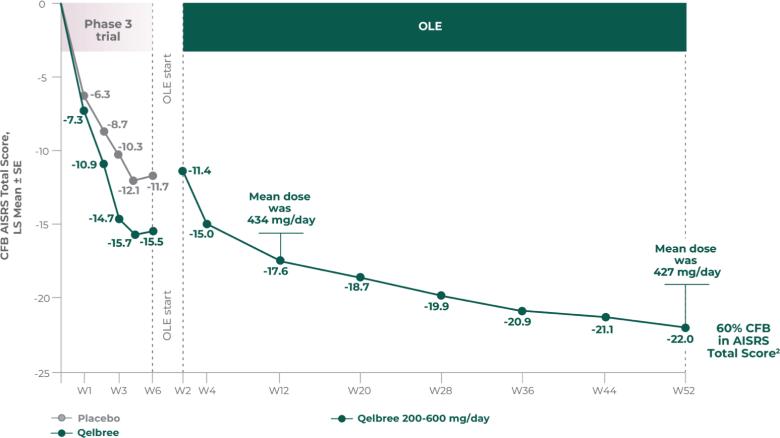
Study P306 EOS=6 weeks.1
Abbreviations: AISRS, ADHD Investigator Symptom Rating Scale; CFB, change from baseline; EOS, end of study.
Simple to start
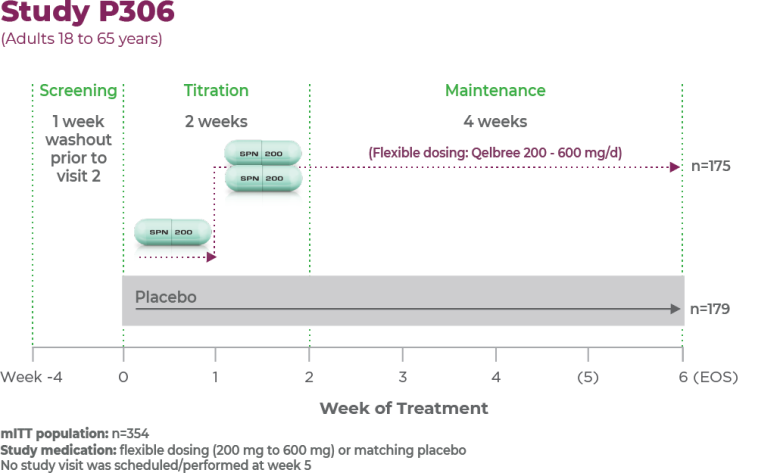
Study P3061
Age group: Adults, 18 to 65 years of age
mITT population: 354
Study medication: Flexible dosing (200 mg to 600 mg) or matching placebo
No study visit was scheduled/performed at week 51,2
Proven efficacy in a robust clinical trial1
Primary efficacy measure: CFB to EOS in AISRS total score vs placebo (N=354)1,2
Qelbree Flexible Dosing Results:
Patients were titrated to receive 200 mg/day for week 1; 400 mg/day for week 2; and from week 3 to EOS, the investigators could titrate up or down by 200 mg/day each week up to 600 mg/day.2
Percentage of patients treated by dose at EOS (n=133)2
Study P306 results:
AISRS Total Score at EOS was significantly reduced in adults treated with Qelbree vs placebo. The CFB in AISRS Total Score at EOS (LS mean ± SE) was -15.5 ± 0.91 for Qelbree and -11.7 ± 0.90 for placebo.1
- Once-daily Qelbree delivers significant symptom score reductions on the subscales of both inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity in adults2
- Once-daily Qelbree demonstrates proven safety and tolerability with no evidence of abuse potential1,2,5
Abbreviations: AISRS, ADHD Investigator Symptom Rating Scale; CFB, change from baseline; EOS, end of study; LS mean, least squares mean; mITT, modified intent to treat; SE, standard error.
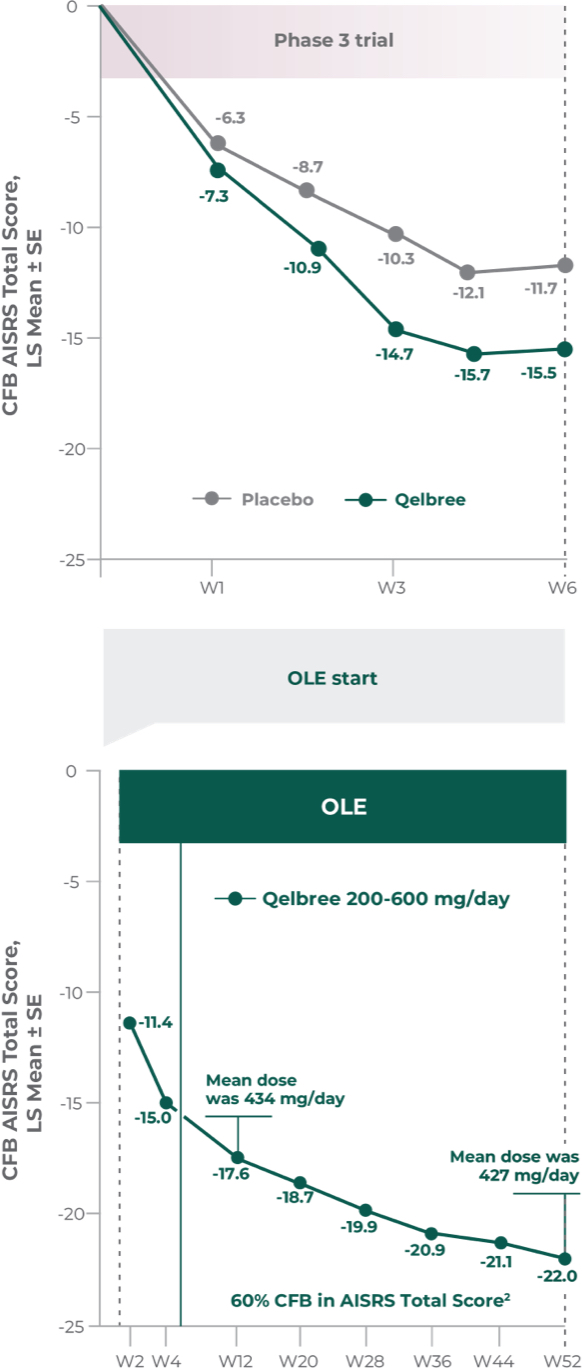
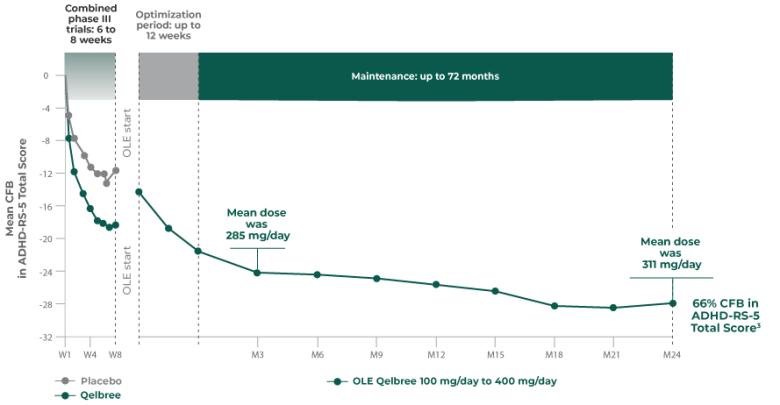
Long-term safety and efficacy trial of Qelbree in adult patients (n=159)2
OLE study (P311): Qelbree 200 mg/day to 600 mg/day2
Methodology2
Open-label, long-term, multicenter, flexible dose study of Qelbree in adults with ADHD who completed Study P306. Subjects received Qelbree 200 mg/day during the first 2 weeks of the study. After Visit 2, Qelbree could be titrated up or tapered by 50 mg increments based on response and tolerability (200 mg/day to 600 mg/day). The number of patients at each time point was: (n=159) at the start of OLE, (n=112) at week 12, and (n=51) at week 52. After week 12, subjects were allowed to use certain approved concomitant ADHD medications (n=9).
Primary objective2
Gather long-term safety data on Qelbree
Secondary objective2
Efficacy data during open-label use.
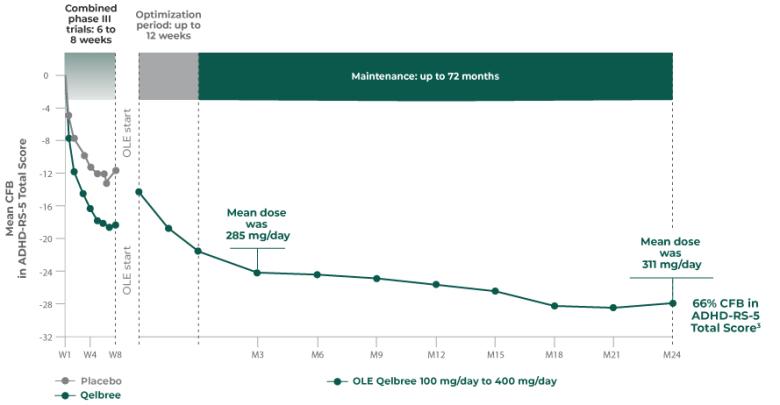
Total daily dose of Qelbree in adults following 52 weeks of treatment in the OLE study2
- OLE mean dose at week 52 was 427 mg/day (n=39)
Long-term data: AISRS Total Score in the OLE analysis at 12 months2
Mean change from baseline in AISRS Total Score2
P311 (OLE): Overall baseline AISRS Total Score was 38.1 for Qelbree
- Data and calculations from patients in the OLE are descriptive only. There is no placebo group from which to draw a comparison of changes from baseline in AISRS Total Score or make any other long-term safety or efficacy conclusions2
- Enrollment in the OLE safety trial was temporarily closed due to COVID-19 pandemic restrictions; therefore, some subjects did not roll over into the OLE immediately after the DB week 6 (EOS) visit
- No new safety signals observed for Qelbree 200 mg/day to 600 mg/day (427 mg/day mean dose at week 52) in the OLE (P311)2
Abbreviations: COVID-19, novel coronavirus disease 2019; DB, double blind; OLE, open-label extension.
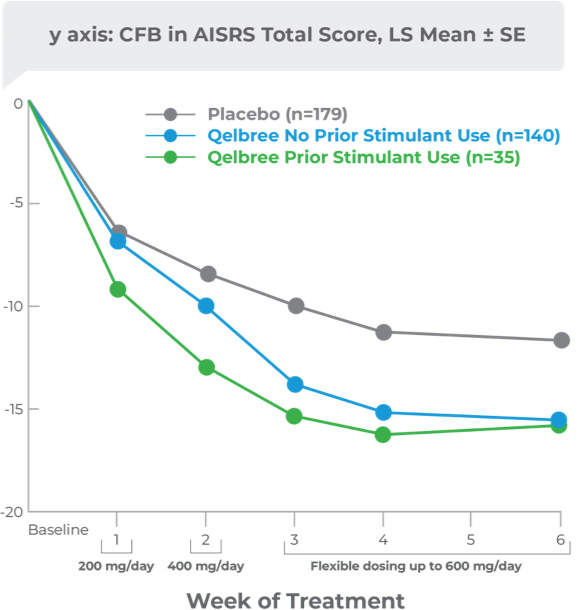
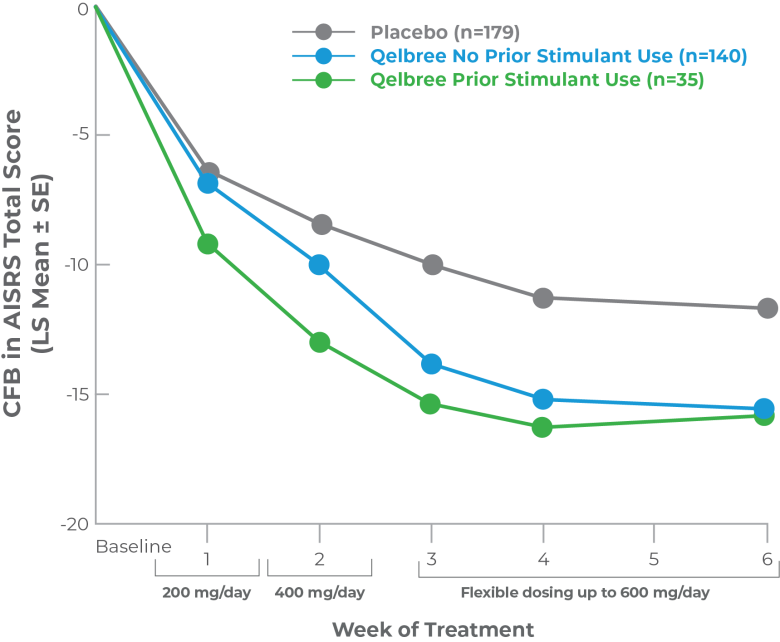
Post hoc analysis: CFB in AISRS Total Score data based on prior stimulant use in adults with ADHD
Methodology2
This post hoc analysis was conducted using phase III trial data (P306) in adults with ADHD. Participants were stratified based on prior history of reported stimulant use (using medication history at enrollment). The purpose of this analysis was to evaluate the CFB in AISRS Total Score for Qelbree based on prior reported stimulant use
Participants using stimulants at the screening visit underwent a ≥1 week washout period before randomization
CFB in AISRS Total Score data based on prior stimulant use at 6 weeks2
- Participants randomized to Qelbree: AISRS scores at week 6 were not statistically different regardless of prior stimulant use2
This analysis was limited by its post hoc nature, including lack of an a priori power analysis, and the small sample size of the prior stimulant user group. These data are descriptive and conclusions cannot be drawn.2

Healthcare providers are widely prescribing Qelbree2
You might also be interested in: