Proven efficacy
Significant reduction in ADHD-RS-5 total score from CFB to EOS (6 weeks)1
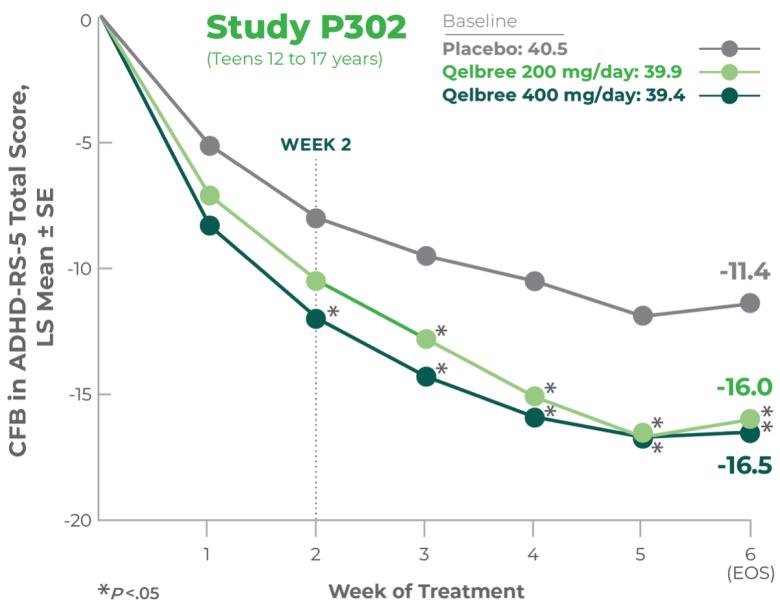
Teens 12 to 17 years of age
Teens 12 to 17 years of age
Inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity symptom score reductions observed as early as week 2.2
Qelbree was studied in 4 clinical trials. In the study of teens 12 to 17 years of age, ADHD symptom score reductions were statistically significant for 400 mg, beginning at week 2.3

Qelbree is the first novel, non-stimulant treatment approved for pediatric ADHD in over a decade1,4-6
ADHD diagnosis based on ADHD-RS-5 screener and DSM-5 criteria
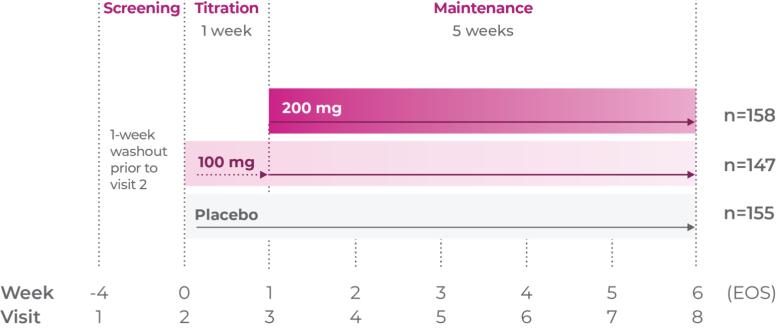
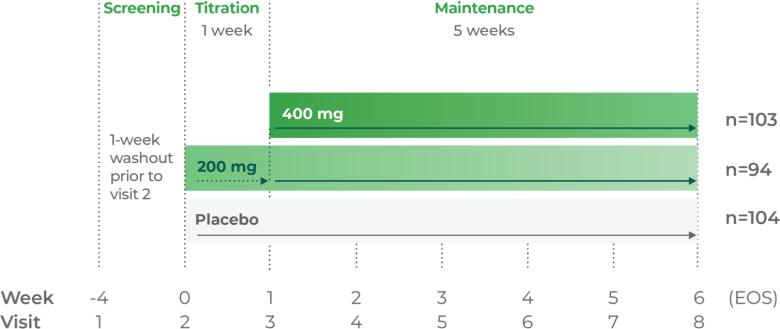
Phase III trial methodology1
The clinical trial was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 3-arm, parallel-group, multicenter study.
Primary endpoint1
CFB in the ADHD-RS-5 total score at EOS, Qelbree treatment group.
Primary analysis is based on mITT population.1,2
Study P302 EOS=Week 6.1
Abbreviations: ADHD-RS-5, Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Rating Scale, 5th ed; CFB, change from baseline; DSM-5, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed; EOS, end of study; mITT, modified intent to treat.
Simple to start1
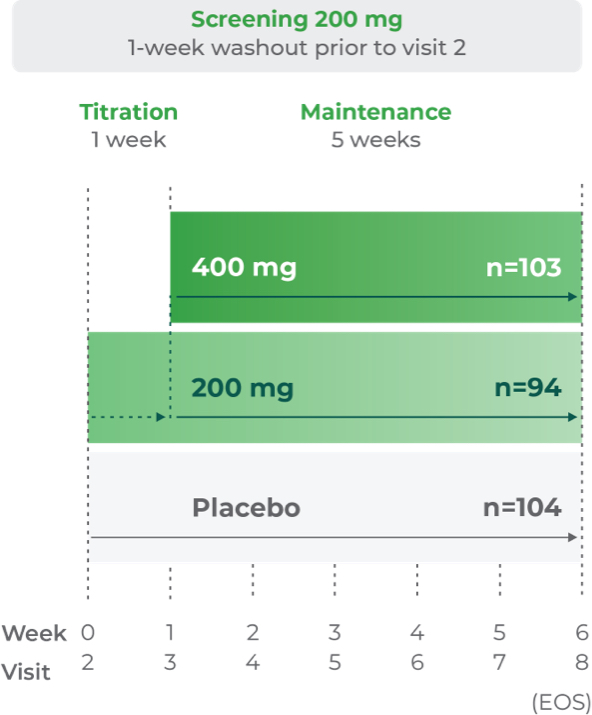
Study P302: Titration at 1 week1,7
Age group: 12 to 17 years of age
mITT population: 301
Study medication: 200 mg capsule or matching placebo
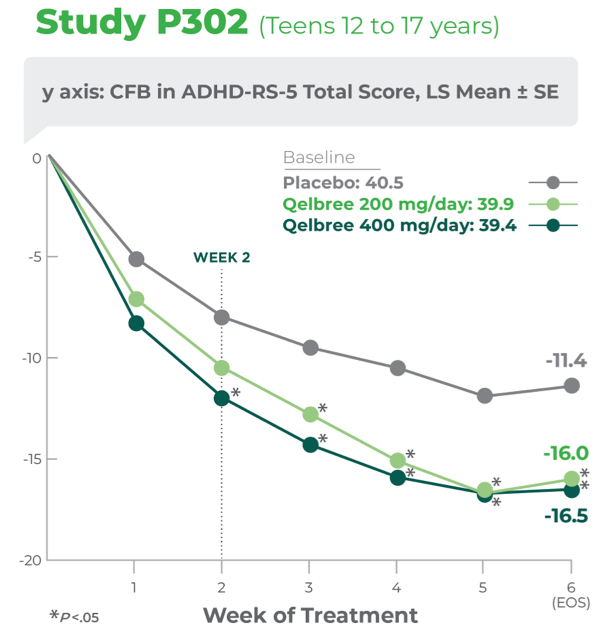
Proven efficacy in a robust clinical trial1
Primary efficacy measure: CFB to EOS on the ADHD-RS-5 Total Score vs placebo (n=301)1,2
Study P302 results:
Total score at EOS was significantly reduced with Qelbree vs placebo. The CFB in ADHD-RS-5 Total Score at EOS (LS mean ± SE) was -16.0 ± 1.45 for Qelbree 200 mg/day, -16.5 ± 1.38 for Qelbree 400 mg/day, and -11.4 ± 1.37 for placebo.
- Once-daily Qelbree delivers significant symptom score reductions on the subscales of both inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity in teens3
- Once-daily Qelbree demonstrates proven safety and tolerability and low discontinuation rates due to AEs in children and teens across clinical trials1,2
Abbreviations: ADHD-RS-5, Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Rating Scale, 5th ed; CFB, change from baseline; EOS, end of study; LS mean, least squares mean; SE, standard error.
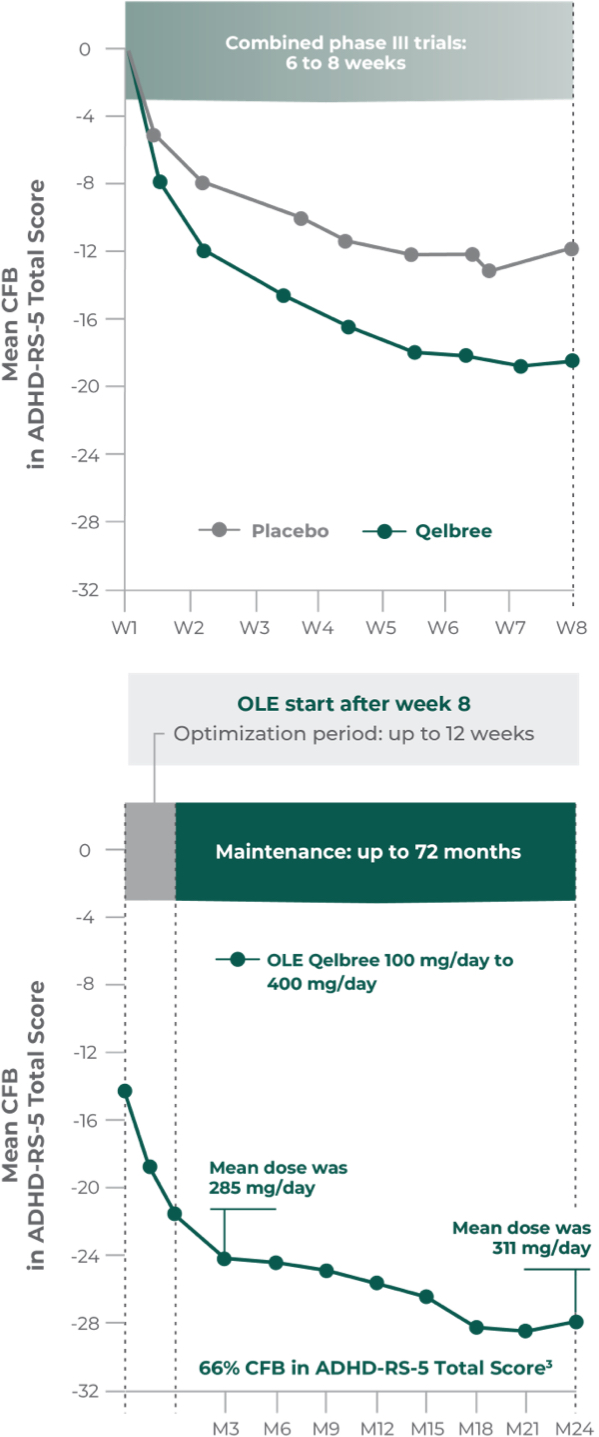
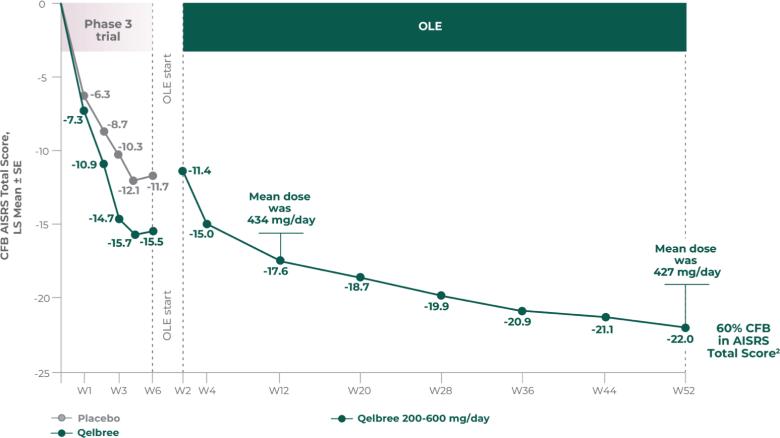
Long-term safety and efficacy trial of Qelbree in children and teens ages 6-17 years with ADHD3
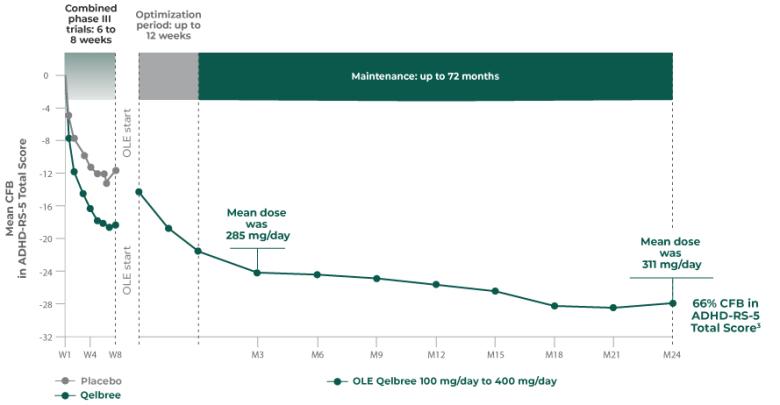
OLE study (P310): Subpopulation analysis, Qelbree 100 mg/day to 400 mg/day3†
Methodology1,3
Open-label, long-term, multicenter, flexible-dose study of Qelbree in children with ADHD who completed a phase II/III trial of Qelbree 100 mg/day to 400mg/day. Patients aged 6 to 11 years began with Qelbree 100 mg/day, adjusted weekly by 100 mg increments based on clinical response (100 mg/day to 400 mg/day). Patients aged 12 to 17 years began with Qelbree 200 mg/day, adjusted weekly by 200 mg increments based on clinical response (200 mg/day to 400 mg/day).†
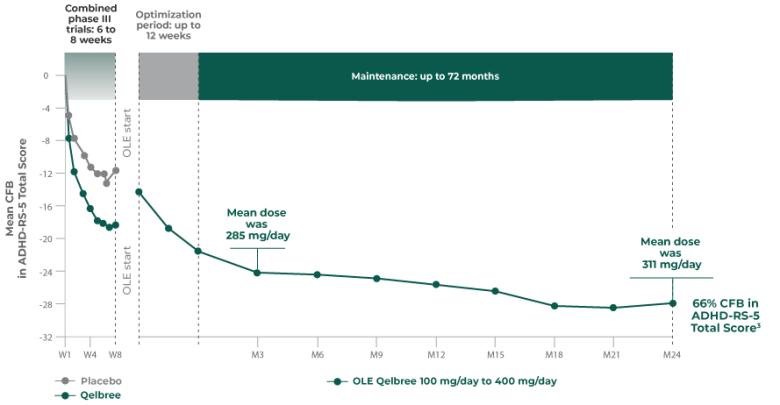
The number of patients at each time point was as follows: entering OLE (n=749), completing optimization period (n=672), month 3 (n=594), month 6 (n=492), month 9 (n=397), month 12 (n=337), and month 24 (n=200). The data presented here include patients who completed visits up to 24 months.
Primary objective3
Gather long-term safety data on Qelbree.
Secondary objective1
Efficacy data during open-label use.
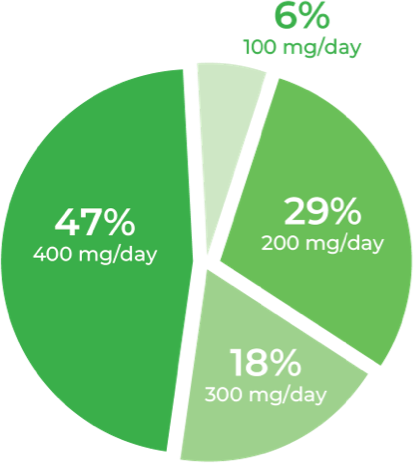
Teens (n=34)
Total daily dose of Qelbree in teens following 24 months of treatment in the OLE study3
Following 24 months of treatment with once-daily Qelbree3:
- 100 mg/day was the least prevalent dose for teens
- Approximately 65% of teens were taking Qelbree 300 to 400 mg/day
†Dose will depend on response to medication. Maximum dose of Qelbree in teens is 400 mg/day.
Long-term data: ADHD-RS-5 Total Score in the OLE subpopulation analysis3
Mean change from baseline in ADHD-RS-5 Total Score3‡
P310 (OLE): Overall baseline ADHD-RS-5 Total Score was 42.9 for Qelbree
- Data and calculations from patients in the OLE are descriptive only. There is no placebo group from which to draw a comparison of changes from baseline in ADHD-RS-5 Total Score or make any other long-term safety or efficacy conclusions3
- OLE start: patients 6 to 11 years of age started on Qelbree 100 mg/day; patients 12 to 17 years of age started on Qelbree 200 mg/day3
Qelbree pediatric OLE subpopulation safety analysis3:
- No new safety signals observed for Qelbree 100 mg/day to 400 mg/day
- 8.1% discontinuation rate due to AEs
‡Based on 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group clinical trials that met the primary endpoint of data in ADHD-RS-5 total symptom score.3
Abbreviations: Abbreviations: AEs, adverse events; LS mean, least squares mean; OLE, open-label extension; SE, standard error.
You might also be interested in: